Physical Education
Gain cognitive content and instruction designed to develop motor skills, knowledge, and behaviors for physical fitness.
Physical Education, B.S.
Bachelor of Science in Physical Education is offered by the College of Behavioral and Health Sciences at MTSU. The major in Physical Education offers preparation for teaching positions in public and private elementary and secondary schools in Tennessee. Students must complete a Secondary Education minor that includes student teaching.
The Physical Education Teaching concentration is unique, placing students as future teachers in several field-based experiences in schools, thus allowing them to begin educating young learners while supervised by a university professor and a public school teacher. No other program in Tennessee and few programs in the country allow the number and quality of supervised field experiences in the schools that MTSU does. If you want a career in which you can enjoy sports and physical activity, and give back to children or youth through teaching or coaching while fulfilling a critical role in helping people achieve a quality level of health, fitness, and skill, MTSU's Physical Education program is right for you. This program has two concentrations: Physical Education Teaching and Sports Pedagogy.
News Briefs
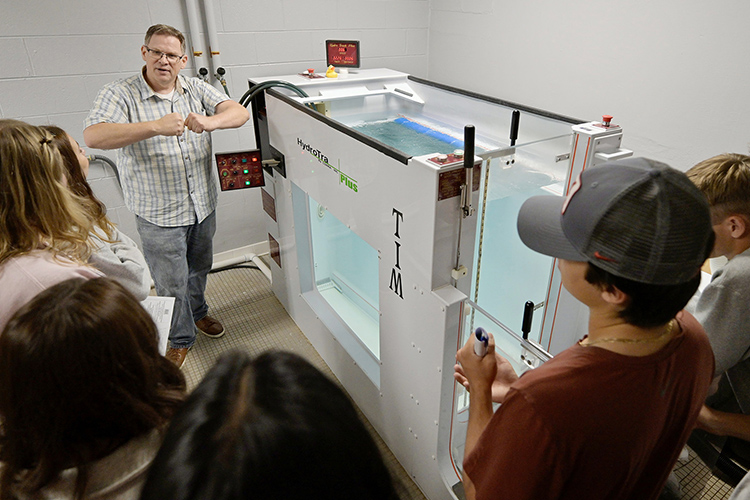

Williamson County high schoolers explore health and human performance degree paths at MTSU
Career and technical education students from Williamson County high schools got a first-rate tour of Department of Health and Human Performance facilities in the College of Behavioral and Health Sciences at Middle Tennessee State University recently. The students enrolled in exercise and health sciences classes at Fairview, Ravenwood and Nolensville high schools learned about potential [ Read More ]
News Briefs

Williamson County high schoolers explore health and human performance degree paths at MTSU
Career and technical education students from Williamson County high schools got a first-rate tour of Department of Health and Human Performance facilities in the College of Behavioral and Health Sciences at Middle Tennessee State University recently. The students enrolled in exercise and health sciences classes at Fairview, Ravenwood and Nolensville high schools learned about potential [ Read More ]
Related Media

Physical Education, B.S.
Physical Education graduates put their skills and knowledge to use in a variety of professions ranging from teaching in various settings to working as therapists to managing others in the field. A variety of examples follow:
Individuals who enter the teaching field are usually offered the option to coach in most schools or districts.
- Elementary physical education teacher
- Middle school physical education teacher
- High school physical education teacher
Physical Education graduates have been hired by school districts all across Tennessee and in surrounding states.
Physical Education graduates have opportunities in various other fields.
Fitness/Health Centers
- Aerobics instructor
- Athletic clubs/center director
- Corporate fitness center manager
- Fitness trainer
- Health or fitness club manager
- Personal fitness trainer
- Somatics instructor
- Strength trainer
- Stress management consultant
- Weight management consultant
Recreation Careers
- Activities instructor
- Aquatics specialist
- Camp instructor/park ranger
- Commercial recreation instructor
- Correctional facilities recreation director
- Dance studio director/instructor
- Facility manager
- Intramural/recreational sports director
- Private clubs' fitness instructor
- Resort activities instructor
- Sports club instructor
- Sports tour operator
- Veterans' hospital recreation director
- Wilderness therapy program director
- YMCA/YWCA activities instructor
Therapy-Related Careers
- Dance therapist
- Movement therapist
- Physical therapist
- Recreational therapist
Coaching/Officiating
- Youth sports
- Interscholastic school sports
- Collegiate sports
- Adult recreation
Other Related Careers
- Emergency services personnel instructor
- Military physical education specialist
- Professional dancer
- Protective services personnel instructor
Professional Associations/Organizations
- Administrative assistant
- Assistant director of administration
- Associate executive director
- Director of communications
- Executive director
- Meeting and event coordinator
- Membership coordinator

MTSU’s Career Development Center
MTSU offers a comprehensive Career Development Center that serves students throughout the full student experience and beyond. They collaborate with faculty and staff to equip students with the tools to be marketable to the world of work and continuing education.
Students can schedule an appointment or check online resources and job boards at mtsu.edu/career.
Students can find current internship opportunities by talking to faculty and visiting the University job and internship board called Handshake.
Wondering what you can do with your major? Check out our What Can I Do with A Major In guides.


Additional Information
- Forms & Manuals
- Resources & Links
Degrees
For complete curriculum details, click on REQUIREMENTS.
Undergraduate
After completing the program requirements in Physical Education Teacher Education, students will obtain a Bachelor of Science (B.S.) degree and K-12 teaching license. Sport Pedagogy graduates will receive a Bachelor of Science (B.S.) degree. Both concentrations consists of 120 credits, which includes 41 hours of General Studies.
Physical Education Teacher Education Program
The Bachelor of Science (B.S.) degree in Physical Education is offered for students seeking a Tennessee K-12 Physical Education Teaching License. The major prepares teacher candidates in the areas of physical education content knowledge, instructional assessment, curriculum planning, and effective pedagogical skills. The program includes courses in the major disciplinary areas of physical education as well as courses that include significant clinical and practical experiences. Students majoring in this concentration are required to pursue a minor in Secondary Education. For more information, contact Dr. Don Belcher ([email protected]).
Sports Pedagogy Concentration
Physical Education is a comprehensive field that engages individuals of all ages, abilities, and cultures in movement experiences that contribute to their growth and development. Physical education is a dynamic field, constantly evolving as societal trends, demographics, and other factors impact upon it. Students majoring in this concentration may choose between a variety of minors (i.e., Athletic Coaching and Officiating, Dance, Health and Somatic Movement). For more information, contact Dr. Don Belcher ([email protected]).
Physical Activities Program
The purpose behind the HHP Department physical activity courses are to introduce students to a variety of lifetime sports, games, and/or activities. Participation in these physical activities is necessary for young adults in college to improve their fitness, skills, and knowledge for safe and satisfactory involvement in these activities over their lifespan. For more information, contact Dr. Bev Clanton ([email protected]).
Students majoring in Physical Education will be required to have a minor in Secondary Education. A second minor can be obtained if an individual is interested in attending additional terms. Other areas of interest for a minor may include health education, coaching, driver's education, and dance. Specific minors offered in the Department of Health and Human Performance are Athletic Coaching and Officiating, Driver and Traffic Safety Education, Communication Disorders, Health, Health and Physical Education, Health and Human Performance, Recreation, Health Care Service, Health Care Administration, and Somatic Movement Education.
Graduate
Students may obtain a MPH degree in Public Health with a concentration in Community Health. The Physical Activity program is designed to enhance the pedagogical skills and knowledge of students who already hold a bachelor's degree in physical education. Students who hold a bachelor's degree in another field may pursue an MHP in Public Health with a concentration in Physical Activity after completing required prerequisite courses. Another option is to combine the MHP program with the post-baccalaureate K-12 licensure program. Students must complete the Ready to Teach program in order to be admitted into the program.
Students may also pursue a Ph.D. in Human Performance with a concentration in Physical Education. The focus of this degree is to transition individuals from physical education teacher to the role of a physical education teacher educator and researcher. See the Physical Education Graduate Program Manager for details.
Other programs offered by HHP
Other undergraduate majors offered by the Health and Human Performance Department that lead to a B.S. include Exercise Science; Public Health; Tourism and Hospitality Management with three concentrations: Event Planning, Hospitality Management, and Tourism Management; Leisure and Sport Management; and Speech-Language Pathology and Audiology.
Other concentrations under the Ph.D. in Human Performance are Exercise Physiology, Health, and Leisure and Sport Management.
In addition, M.S. degrees are available with a major in Exercise Physiology and a major in Leisure, Sport, and Tourism Management with a choice of concentrations in Recreation and Leisure Services and Sport Industry.
Professional Licensure Disclosure
MTSU discloses that the Bachelor of Science (BS) in Physical Education is a teacher licensure preparation program accredited by the Council for the Accreditation of Educator Preparation (CAEP) and approved by the Tennessee Department of Education. Admission to an undergraduate teacher licensure preparation program does not guarantee that students will obtain a teacher license. Successful completion of the program meets the educational requirements to apply for a practitioner teacher licensure in Tennessee.
The BS Physical Education disclosure provided on MTSU’s professional licensure disclosure website indicates the states and territories where MTSU has determined, through reasonable and good faith effort, that the program does or does not meet the educational requirements for other US states and territories. Licensing authorities for each state set and enforce their own requirements and standards, which are subject to change. Current and prospective students not located in Tennessee or who plan to seek licensure or certification outside the state of Tennessee should contact the appropriate state licensing agency or board and discuss their plans with an advisor and the MTSU Office of Teacher Licensure before enrolling in the program to ensure they have the most up-to-date information and guidance regarding licensure requirements
Related Links
CONTACT US