Journalism
Media Studies provides an in-depth understanding of film, TV, advertising, and media's impact on society.
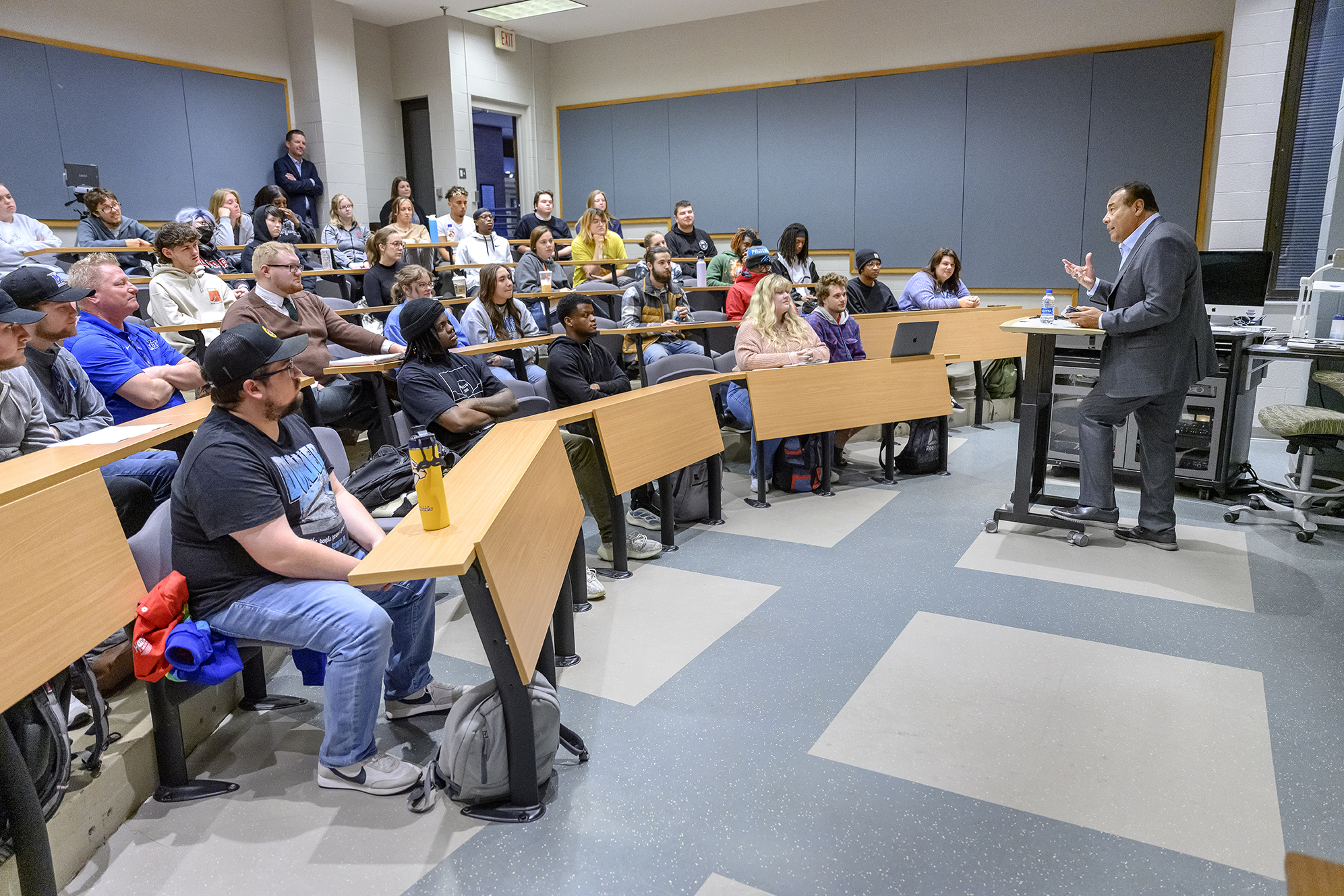
Journalism, Media Studies Concentration, B.S.
The Media Studies degree is designed for students who enjoy discussing, analyzing, and writing about film, television, advertising, and other media. In this concentration, students think about the interplay between media and society, exploring the messages in historical and contemporary media content, as well as examining how and why media influence audience perception and behavior. The Media Studies concentration in Journalism is designed for students who enjoy discussing, analyzing, and writing about film, TV, advertising, and other media. The Media Studies degree is ideal for those interested in a liberal arts approach to mass communication, especially if planning to pursue graduate studies. Students will participate in academic media research and writing. Majors examine media messages in historical and contemporary media, plus critique visual images and their impact on society. They also explore how and why media influence audience perception and behavior.
The Media Studies concentration in the Bachelor of Science in Journalism program is offered through the School of Journalism and Strategic Media in the Scott Borchetta College of Media and Entertainment at MTSU.
News Briefs

MTSU on WGNS: Police bike training, changing media landscape, book on death, burial in the South
MTSU representatives appeared on WGNS Radio recently to talk about recent bicycle patrol training of campus and local police officers, training students for the changing media landscape, and a new book about the 20th century customs surrounding health, death and burial in the South. They appeared on the live “Action Line” program with host Scott Walker [ Read More ]
News Briefs

MTSU on WGNS: Police bike training, changing media landscape, book on death, burial in the South
MTSU representatives appeared on WGNS Radio recently to talk about recent bicycle patrol training of campus and local police officers, training students for the changing media landscape, and a new book about the 20th century customs surrounding health, death and burial in the South. They appeared on the live “Action Line” program with host Scott Walker [ Read More ]
Related Media

Journalism, Media Studies Concentration, B.S.
The Journalism major prepares students who wish to be journalists for a number of jobs in the media. The sequence helps graduates attain careers with newspapers, trade and consumer magazines, book publishing, websites, multimedia, public relations firms, health care, education, advertising, television, radio, film and video production, and other professional media organizations. Journalism professionals can literally go as far as they want, from small media companies to larger outlets that include travel all over the world. Possible professional positions to pursue include
- Advertising executive
- Arts/entertainment critic
- Author/novelist
- Book editor
- Business communications specialist
- Copy editor
- Editorial writer
- Editor
- Feature writer
- Freelance magazine writer
- Graphic designer
- Media website entrepreneur
- News reporter
- Online or multiplatform journalist
- Photojournalist
- Public relations/marketing manager
- Radio/TV broadcaster
- Scriptwriter/playwright
- Sports journalist
- Television/radio/video producer
- Textbook editor/writer
- Trade publication editor/writer
Employers of MTSU media studies degree alumni include
- Associated Press
- Atlanta Journal-Constitution
- Chattanooga Times-Free Press
- CityPress Communications/Nashville Scene
- CJ Advertising
- Daily News Journal (Murfreesboro)
- Daily Oklahoman
- Detroit Free Press
- Gallatin News-Examiner
- Gannett Design Studio
- Journal Communications
- LifeWay Christian Resources
- Murfreesboro Post
- Murfreesboro Pulse
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- Professional Bull Riders Inc.
- Raleigh News & Observer
- South Central Media
- The Tennessean (Nashville)
- Travelocity
- Warner Music Nashville
- WPLN-FM public radio
- WSMV-Channel 4 (Nashville)
- WTVF-Channel 5 (Nashville)

MTSU’s Career Development Center
MTSU offers a comprehensive Career Development Center that serves students throughout the full student experience and beyond. They collaborate with faculty and staff to equip students with the tools to be marketable to the world of work and continuing education.
Students can schedule an appointment or check online resources and job boards at mtsu.edu/career.
Students can find current internship opportunities by talking to faculty and visiting the University job and internship board called Handshake.
Wondering what you can do with your major? Check out our What Can I Do with A Major In guides.


Degrees
MTSU’s School of Journalism and Strategic Media offers a Bachelor of Science (B.S.) degree with a major in Advertising and Public Relations or Journalism.
Concentrations within Advertising and Public Relations include:
Concentrations within Journalism include:
- Entertainment Journalism
- Environmental Journalism and Communication
- Investigative Journalism
- Media Design
- Media Studies
- Sports Media
For complete curriculum details, click on REQUIREMENTS.
Undergraduate or graduate students outside the College of Media and Entertainment may choose to minor in Mass Communication with an emphasis in any of the School of Journalism and Strategic Media’s concentrations.
A Master of Science (M.S.) degree is available in Media and Communication.
Accreditation Equals Excellence
About 1,000 schools across the US offer study in journalism, public relations or some form of media. Only 112 of these are accredited journalism and media programs. We’re proud that MTSU is one of these.
Accreditation is a voluntary self-assessment and external review by educators and media professionals. The reviewers examine program resources, classes and student success. Every six years, MTSU’s program is measured against national standards to ensure that we’re offering the best, most up-to-date experience we can provide. Accreditation provides an assurance of quality to students, parents, and the public.
The MTSU School of Journalism and Strategic Media was found in full compliance on all nine accreditation standards.
Go to the Accrediting Council on Education in Journalism and Mass Communication for more information about the value of accreditation.
Our Mission Statement
The School of Journalism and Strategic Media’s mission statement is comprised of five key points:
- Provide an undergraduate education combining contemporary media instruction with hands-on professional experience.
- Educate students about the role and responsibilities of a free press and media in a democratic and diverse society.
- Prepare students for careers in journalism, communication, and strategic media in an ever-evolving media environment.
- Contribute to the body of knowledge in journalism, communication, and strategic media through research, scholarship, creative, and professional activity.
- Create an inclusive environment that celebrates diversity in its curriculum, organizations, and community engagement through its students, faculty, staff, and alumni.
A PDF copy of the Mission Statement can be downloaded here.
Our Strategic Plan
The SoJSM’s Strategic Plan can be viewed here.
Our Assessment Plan
The SoJSM’s Assessment Plan can be viewed here.
Data
In the spirit of sharing information related to the program’s performance with the public, the following data is provided:
- New Freshmen Fall-to-Fall Retention
- Undergraduate Fall-to-Fall Retention
- 4-year Graduation Rates
- 6-year Graduation Rates
- Degrees Awarded by Academic Year
- Student Learning Outcomes
Related Links
CONTACT US